
Rotary engines are often referenced to as the Wankel engine in honor of its inventor. Felix Wankel performed most of the research and development leading to the first running prototype in early 1957.
This rotating piston design is similar to standard gasoline engines in that the spark plug ignites the air fuel mixture on the compression cycle.
Although keep in mind that its internal design is quite different than reciprocal gas motors. I added a video at the bottom that shows the insides and the rotational movement that can help make sense of this design.
The rotary gets its name from the rotating motion of the large triangular shaped piston that is often called a rotor instead of a piston. In addition, it uses ports rather than valves for controlling the intake of the air fuel mixture and the exhausting of combusted gases.
The heart of a rotary engine is a triangular shaped rotor that walks around a smaller rigidly mounted gearing assembly. This is connected to the crankshaft through additional gears in such a manner that, for every rotation of the rotor the crankshaft revolves three times.
This is one of the reasons for very high engine RPM . In fact some of these motors will have red-lines between 10 and 12 thousand revaluations per minute. It also takes much less torque to turn over this type of automotive engine as compared to its conventional reciprocating cousins.
The tips of the triangular piston move within the housing and are in constant contact with the walls of the cylinder housing causing a tight seal. As the assembly moves, the volume between each side of the rotor and the housing walls continually changes. In the picture below is an illustration of the four cycles.
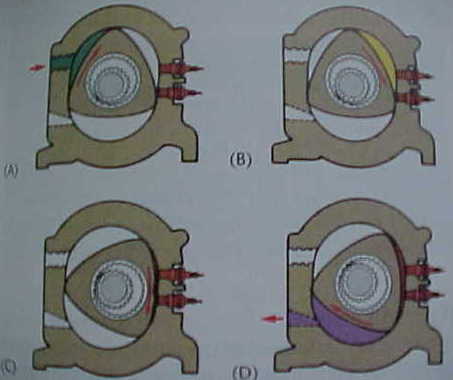
In the illustration, above the intake port is uncovered and the air fuel mixture is entering the upper chamber colored in green picture (a). As the rotor moves to position (B), the intake port closes and the upper chamber reaches its maximum volume.
When full compression is reached, as in figure (C), the spark plugs fire one after the other to start the power stroke.
In position, (D). the side of the rotor uncovers the exhaust port and exhaust gases are expelled in purple.
This cycle continues until position and is reached in the intake cycle begins again. The fact that the rotating combustion chamber engine is small and light for the amount of power it produces makes it an attractive power plant for smaller automobiles.
Mazda Rotary Engines
After a few years of not offering a Wankel engine sports car Mazda has released a redesigned rotary engine for their RX8. I was working at a local Mazda dealer when this thing hit the market.
Although the engine had its share of problems mostly stemming from cold start issues, the smoothness and the power are very unique. With a motorcycle like red line of around 9,000 RPMs and base horsepower produced around 200, the RX8 is an exciting car to drive.
My most vivid memory of working on this motor is when I had the pleasure of replacing one in a black RX8 under warranty. The block itself weighed around 15 or 20 pounds due to it’s all aluminum construction and large coolant jackets.
After removing and stripping it, I was carrying just the engine block around the shop and throwing it to other mechanics. The look on their faces as the aluminum block headed their way was priceless. This next Wankel video is pretty amazing. At the time of this post it has a 5 star rating on you tube. And you know how tough people can be with their ratings.
Video of a Wankel Going Through the Motions
If you would like to learn more about different types of automotive power trains take a minute and visit my page about how automotive engines work.
Find out what else is cover on this car repair website on the home page. This next link takes you from rotary engines to car repair answers.

